Guide Contents
Using Canary Tokens: The basic principles
Canary tokens detect intruders by tricking intruders into thinking they are real access tokens (passwords) that can be used to gain further access. In fact they provide no access at all, and when a hacker tries to use the token they are detected. How and where the tokens are placed is critical to their effectiveness.
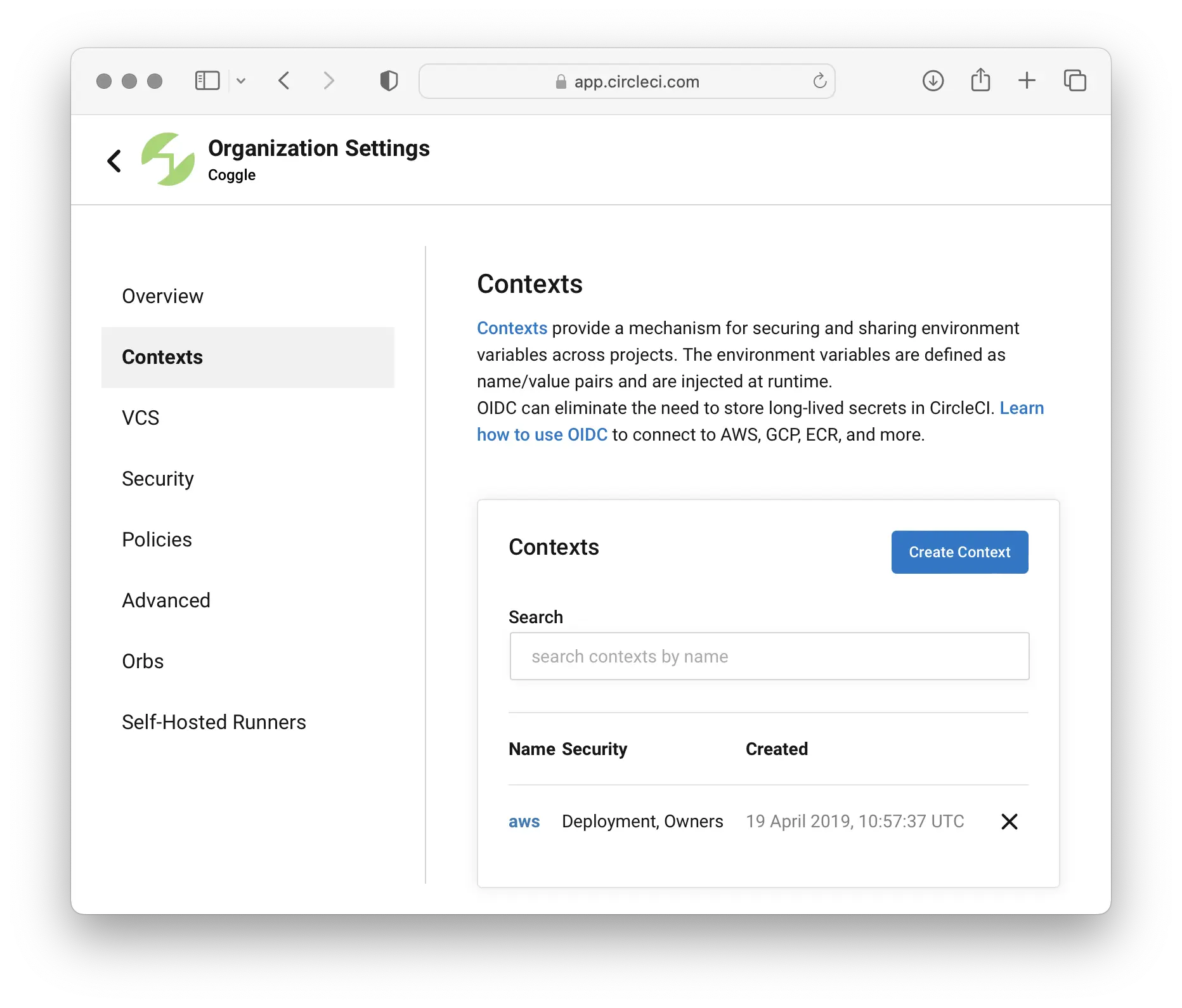
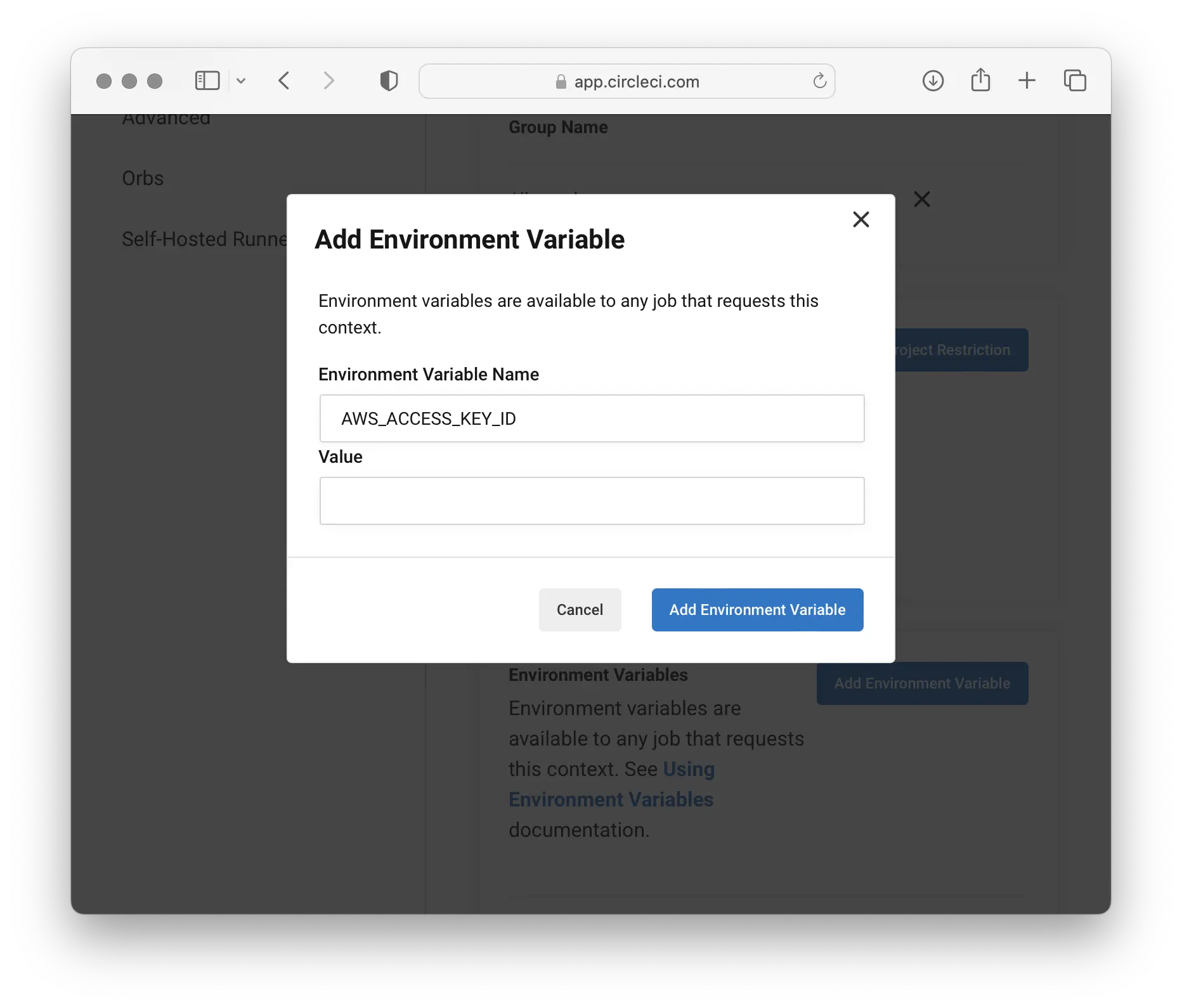
Each canary token is a genuine set of AWS credentials: an AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID along with an AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY.
These need to be discoverable to an intruder looking for access keys, but they also mustn't be accidentally used by a genuine application (which would cause false positive alerts to be sent, and may disrupt the application).
Canary tokens should not be in placed deliberately public locations (such as the client-side code of a mobile app).
Use unique tokens
It's important that canary tokens are specific to individual security domains. Use a unique token for a single group of servers that run the same application, and a different token for each third party application.
This means that when an alert about token is sent, you can identify which system has been compromised from the token.
It is more useful to place a canary token alongside the other configuration or secrets for an application, such as in instance data or a parameter store vault for an cloud server, rather than including it a base container image used by many different applications.
You understand your company any applications best, so following these principles you can place your canary tokens wherever you like. However these are our suggestions to get started: